import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
show_animation = True
class AStarPlanner:
def __init__(self, ox, oy, reso, rr):
"""
Initialize grid map for a star planning
ox: x position list of Obstacles [m]
oy: y position list of Obstacles [m]
reso: grid resolution [m]
rr: robot radius[m]
"""
self.reso = reso
self.rr = rr
self.calc_obstacle_map(ox, oy)
self.motion = self.get_motion_model()
class Node:
def __init__(self, x, y, cost, pind):
self.x = x # index of grid
self.y = y # index of grid
self.cost = cost
self.pind = pind
def __str__(self):
return str(self.x) + "," + str(self.y) + "," + str(self.cost) + "," + str(self.pind)
def planning(self, sx, sy, gx, gy):
"""
A star path search
input:
sx: start x position [m]
sy: start y position [m]
gx: goal x position [m]
gx: goal x position [m]
output:
rx: x position list of the final path
ry: y position list of the final path
"""
nstart = self.Node(self.calc_xyindex(sx, self.minx),
self.calc_xyindex(sy, self.miny), 0.0, -1)
ngoal = self.Node(self.calc_xyindex(gx, self.minx),
self.calc_xyindex(gy, self.miny), 0.0, -1)
open_set, closed_set = dict(), dict()
# populate the frontier (open set) with the starting node
open_set[self.calc_grid_index(nstart)] = nstart
while 1:
if len(open_set) == 0:
print("Open set is empty..")
break
c_id = min(
open_set, key=lambda o: open_set[o].cost + self.calc_heuristic(ngoal, open_set[o]))
current = open_set[c_id]
# show graph
if show_animation: # pragma: no cover
plt.plot(self.calc_grid_position(current.x, self.minx),
self.calc_grid_position(current.y, self.miny), "xc")
# for stopping simulation with the esc key.
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect('key_release_event',
lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
if len(closed_set.keys()) % 10 == 0:
plt.pause(0.001)
if current.x == ngoal.x and current.y == ngoal.y:
print("Find goal")
ngoal.pind = current.pind
ngoal.cost = current.cost
break
# Remove the item from the open set
del open_set[c_id]
# Add it to the closed set
closed_set[c_id] = current
# expand_grid search grid based on motion model
for i, _ in enumerate(self.motion):
node = self.Node(current.x + self.motion[i][0],
current.y + self.motion[i][1],
current.cost + self.motion[i][2], c_id)
n_id = self.calc_grid_index(node)
# If the node is not safe, do nothing
if not self.verify_node(node):
continue
if n_id in closed_set:
continue
if n_id not in open_set:
open_set[n_id] = node # discovered a new node
else:
if open_set[n_id].cost > node.cost:
# This path is the best until now. record it
open_set[n_id] = node
rx, ry = self.calc_final_path(ngoal, closed_set)
return rx, ry
def calc_final_path(self, ngoal, closedset):
# generate final course
rx, ry = [self.calc_grid_position(ngoal.x, self.minx)], [
self.calc_grid_position(ngoal.y, self.miny)]
pind = ngoal.pind
while pind != -1:
n = closedset[pind]
rx.append(self.calc_grid_position(n.x, self.minx))
ry.append(self.calc_grid_position(n.y, self.miny))
pind = n.pind
return rx, ry
@staticmethod
def calc_heuristic(n1, n2):
w = 1.0 # weight of heuristic
d = w * math.hypot(n1.x - n2.x, n1.y - n2.y)
return d
def calc_grid_position(self, index, minp):
"""
calc grid position
:param index:
:param minp:
:return:
"""
pos = index * self.reso + minp
return pos
def calc_xyindex(self, position, min_pos):
return round((position - min_pos) / self.reso)
def calc_grid_index(self, node):
return (node.y - self.miny) * self.xwidth + (node.x - self.minx)
def verify_node(self, node):
px = self.calc_grid_position(node.x, self.minx)
py = self.calc_grid_position(node.y, self.miny)
if px < self.minx:
return False
elif py < self.miny:
return False
elif px >= self.maxx:
return False
elif py >= self.maxy:
return False
# collision check
if self.obmap[node.x][node.y]:
return False
return True
def calc_obstacle_map(self, ox, oy):
# map limits
self.minx = round(min(ox))
self.miny = round(min(oy))
self.maxx = round(max(ox))
self.maxy = round(max(oy))
print("minx:", self.minx)
print("miny:", self.miny)
print("maxx:", self.maxx)
print("maxy:", self.maxy)
self.xwidth = round((self.maxx - self.minx) / self.reso)
self.ywidth = round((self.maxy - self.miny) / self.reso)
print("xwidth:", self.xwidth)
print("ywidth:", self.ywidth)
# obstacle map generation
self.obmap = [[False for i in range(self.ywidth)]
for i in range(self.xwidth)]
for ix in range(self.xwidth):
x = self.calc_grid_position(ix, self.minx)
for iy in range(self.ywidth):
y = self.calc_grid_position(iy, self.miny)
for iox, ioy in zip(ox, oy):
d = math.hypot(iox - x, ioy - y)
if d <= self.rr:
self.obmap[ix][iy] = True
break
@staticmethod
def get_motion_model():
# dx, dy, cost
motion = [[1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1],
[-1, 0, 1],
[0, -1, 1],
[-1, -1, math.sqrt(2)],
[-1, 1, math.sqrt(2)],
[1, -1, math.sqrt(2)],
[1, 1, math.sqrt(2)]]
return motion
def main():
print(__file__ + " start!!")
# start and goal position
sx = 10.0 # [m]
sy = 10.0 # [m]
gx = 50.0 # [m]
gy = 50.0 # [m]
grid_size = 2.0 # [m]
robot_radius = 1.0 # [m]
# set obstable positions
ox, oy = [], []
for i in range(-10, 60):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(-10.0)
for i in range(-10, 60):
ox.append(60.0)
oy.append(i)
for i in range(-10, 61):
ox.append(i)
oy.append(60.0)
for i in range(-10, 61):
ox.append(-10.0)
oy.append(i)
for i in range(-10, 40):
ox.append(20.0)
oy.append(i)
for i in range(0, 40):
ox.append(40.0)
oy.append(60.0 - i)
if show_animation: # pragma: no cover
plt.plot(ox, oy, ".k")
plt.plot(sx, sy, "og")
plt.plot(gx, gy, "xb")
plt.grid(True)
plt.axis("equal")
a_star = AStarPlanner(ox, oy, grid_size, robot_radius)
rx, ry = a_star.planning(sx, sy, gx, gy)
if show_animation: # pragma: no cover
plt.plot(rx, ry, "-r")
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
A* Planner in Python
A stand-alone A* planner in python is shown next. Its instructive to go through the code to understand how it works.
Executing the code above results in the animation:
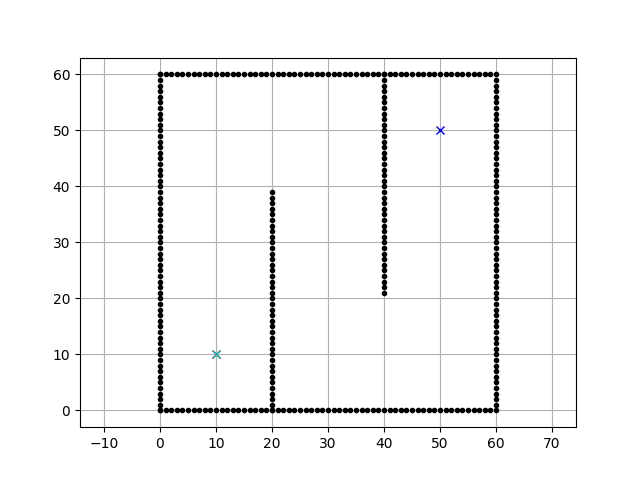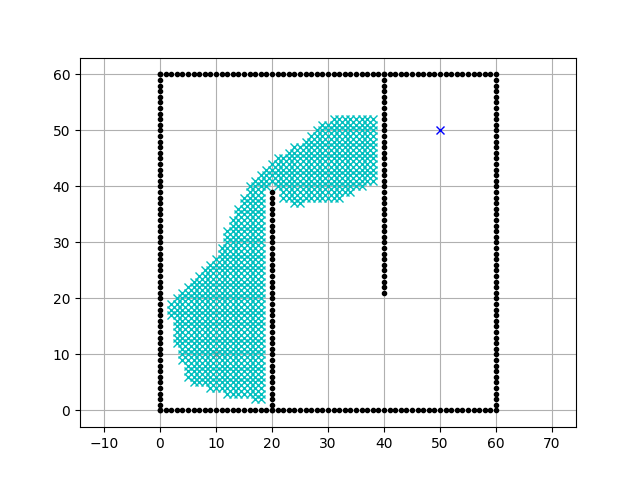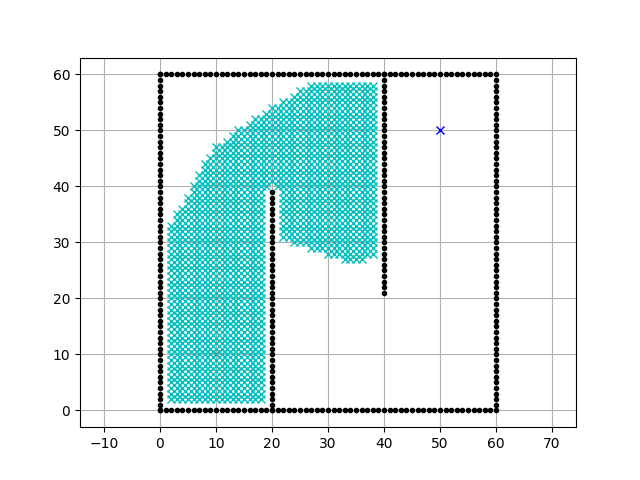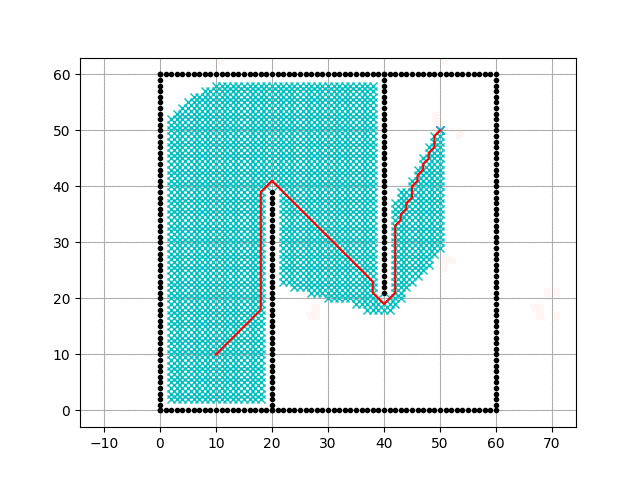
Animation of the A* algorithm - from here