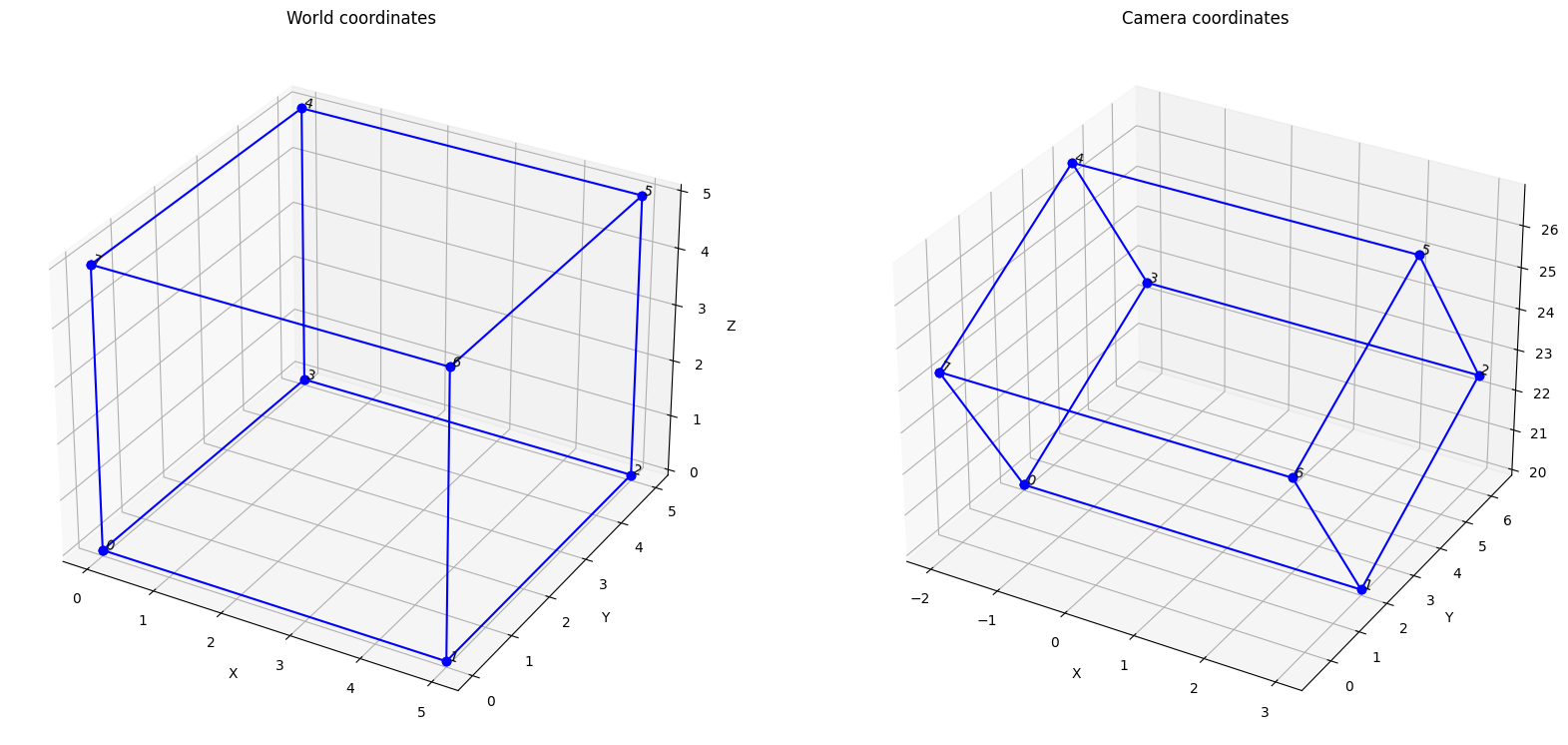
''' Code to generate the 2D image locations given the 3D world coordinates, illustrated using points on a cube, '''
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#-------------------------Some support functions------------------------------------
def rotation_euler (theta_x, theta_y, theta_z) :
# a function that returns a 3 by 3 rotation matrix given the Euler rotation angles in radians.
R_x = np.array([[1, 0, 0], [0, np.cos(theta_x), -np.sin(theta_x)], [0, np.sin(theta_x), np.cos(theta_x)]])
R_y = np.array([[np.cos(theta_y), 0, -np.sin(theta_y)], [0, 1, 0], [np.sin(theta_y), 0, np.cos(theta_y)]])
R_z = np.array([[np.cos(theta_z), -np.sin(theta_z), 0], [np.sin(theta_z), np.cos(theta_z), 0], [0, 0, 1]])
print('R_x=\n', R_x, '\nR_y=\n', R_y, '\nR_z=\n', R_z)
return(R_x @ R_y @ R_z)
def plot_cube (axis, p_t) :
# Given 8 vertices (p_t is 8 by 4 by 1), plot the 3D cube edges and vertices
axis.plot3D(p_t[:,0,0], p_t[:,1,0], p_t[:,2,0], c='b', marker='o')
axis.plot3D([p_t[0,0,0], p_t[7,0,0]], [p_t[0,1,0], p_t[7,1,0]], [p_t[0,2,0], p_t[7,2,0]], c='b', marker='o')
axis.plot3D([p_t[2,0,0], p_t[5,0,0]], [p_t[2,1,0], p_t[5,1,0]], [p_t[2,2,0], p_t[5,2,0]], c='b', marker='o')
axis.plot3D([p_t[1,0,0], p_t[6,0,0]], [p_t[1,1,0], p_t[6,1,0]], [p_t[1,2,0], p_t[6,2,0]], c='b', marker='o')
axis.plot3D([p_t[0,0,0], p_t[3,0,0]], [p_t[0,1,0], p_t[3,1,0]], [p_t[0,2,0], p_t[3,2,0]], c='b', marker='o')
axis.plot3D([p_t[4,0,0], p_t[7,0,0]], [p_t[4,1,0], p_t[7,1,0]], [p_t[4,2,0], p_t[7,2,0]], c='b', marker='o')
axis.set_xlabel('X')
axis.set_ylabel('Y')
axis.set_zlabel('Z')
for i in range(8):
axis.text(p_t[i,0,0], p_t[i,1,0], p_t[i,2,0], '{}'.format(i), 'x')
#---------------------------------------------------------------
# Generate 8 vertices of a 5 by 5 by 5 sized cube with one of the vertices at origin of the world coordinates (homogenous)
N = 8
p_tilde = np.array([[0, 0, 0, 1], [5, 0, 0, 1], [5, 5, 0, 1], [0, 5, 0, 1], [0, 5, 5, 1], [5, 5, 5, 1], [5, 0, 5, 1], [0, 0, 5, 1]])
p_tilde = np.expand_dims(p_tilde, 2) # the dimension for p_tilde will change from (N by 4) to (N by 4 by 1)
print('Dimensions of p_tilde:', p_tilde.shape)
#---------------------------------------------------------------
# plot the cube, with respect to the world coordinates
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,2,1, projection='3d')
plot_cube (ax, p_tilde)
ax.set_title('World coordinates')
#---------------------------------------------------------------
# Setup the camera rotation and translation with respect to the world coordinates
R = rotation_euler(30*np.pi/180, 0, 0)
T = np.array([-2,2,20])
P = np.eye(4)
P[0:3,0:3] = R
P[0:3,3] = T
print('R=\n', R, '\nT=\n', T, '\nP=\n', P)
#---------------------------------------------------------------
# Transform the 3D coordinates from world to camera coordinates
p_c_tilde = P @ p_tilde # @ is matrix multiply in python
# P is 4 by 4 and p_tilde is 8 by 4 by 1, so this is not a standard matrix multiply!
# It is using a feature called broadcasting. It will effectively multiple each
# of the 4 by 1 homogeneous point representations by the 4 by 4 matrix to
# result in a 8 by 4 by 1 output.
'''
NUMPY BROADCASTING -- very important feature
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/numpy/numpy_broadcasting.htm
https://numpy.org/devdocs/user/basics.broadcasting.html
'''
#---------------------------------------------------------------
# plot the points in camera coordinates
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,2,2, projection='3d')
plot_cube (ax, p_c_tilde)
ax.set_title('Camera coordinates')