import numpy as np
def deterministic_robot_cleaning_v1():
# Initialization
state = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] # Set of states
action = [-1, 1] # Set of actions
Q = np.zeros((len(state), len(action))) # Initial Q can be chosen arbitrarily
Qold = Q # Save a backup to compare later
L = 15 # Number of iterations
gamma = 0.5 # Discounting factor
epsilon = 0.001 # Final error to stop the algorithm
# Deterministic Q-iteration algorithm
for l in range(1, L + 1):
print(f'iteration: {l}')
for ii in range(len(state)):
for jj in range(len(action)):
Q[ii, jj] = reward(state[ii], action[jj]) + gamma * Q[model(state[ii], action[jj]), jj]
if np.abs(np.sum(Q - Qold)) < epsilon:
print('Epsilon criteria satisfied!')
break
else:
# print(Q) # Show Q matrix in each iteration
Qold = Q
# Show the final Q matrix
print('Q matrix (optimal):')
print(Q)
C = np.argmax(Q, axis=1) # Finding the max values
print('Q(optimal):')
print(C)
print('Optimal Policy:')
print('*')
print([action[C[1]], action[C[2]], action[C[3]], action[C[4]]])
print('*')
# This function is the transition model of the robot
# The inputs are: the current state, and the chosen action
# The output is the next state
def model(x, u):
if 2 <= x <= 5:
return x + u
else:
return x
# This function is the reward function for the task
# The inputs are: the current state, and the chosen action
# The output is the expected reward
def reward(x, u):
if x == 5 and u == 1:
return 5
elif x == 2 and u == -1:
return 1
else:
return 0
# Call the main function
deterministic_robot_cleaning_v1()Cleaning Robot - Deterministic MDP
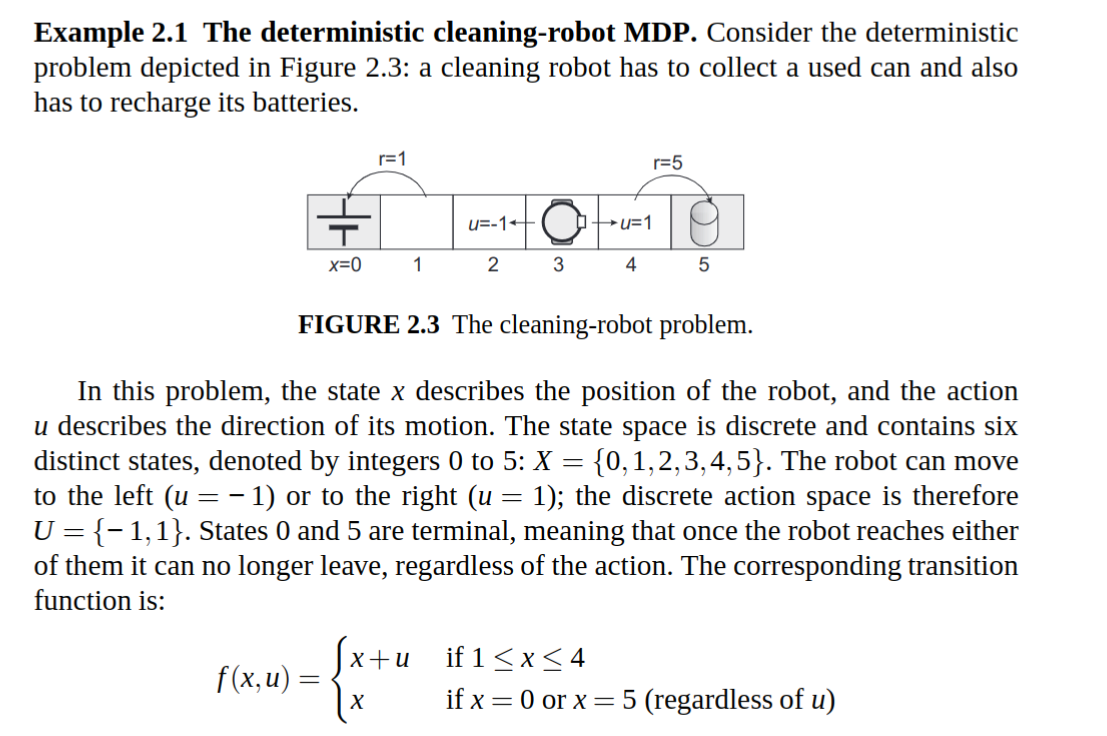
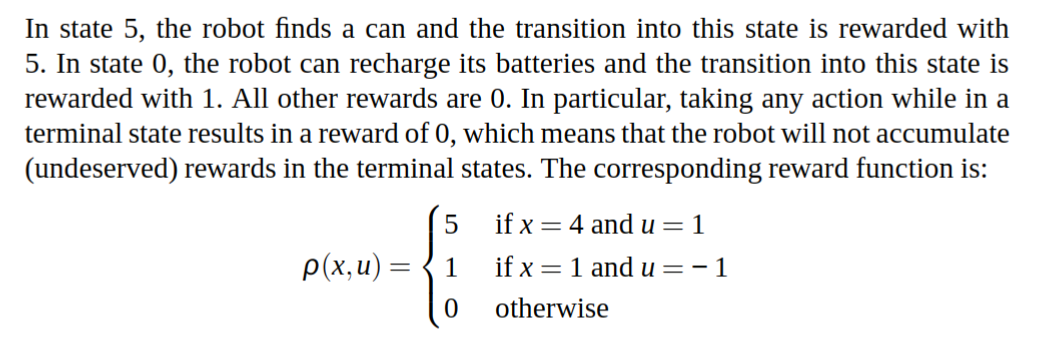
The following code shows the estimation of the q value function for a policy, the optimal q_star and the optimal policy for the cleaning robot problem in the deterministic case.